

- BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 HOW TO
- BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 REGISTRATION
- BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 SOFTWARE
8:00am-10:30am – Yoga, Breakfast, networking, tabling, bookstore.

BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 REGISTRATION
BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 HOW TO
He is also the author of Making It Up As We Go Along, the Story of the Albany Free School (Heinemann 1998), Teaching the Restless, One School's Remarkable No-Ritalin Approach to Helping Children Learn and Succeed (Beacon Press 2004), How to Grow a School: Starting and Sustaining Schools That Work (Oxford Village Press 2006), and In Defense of Childhood: Protecting Kids’ Inner Wildness (Beacon Press 2007).Ĭurrently Chris is a regular columnist for Encounter magazine. He is a member of AERO's Board of Directors.
BRAIN GYM CONFERENCE 2013 SOFTWARE
Data were analyzed by multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA) with SPSS software version 25.Chris Mercogliano was a teacher at the Albany Free School for thirty-five years and stepped down as director in June 2007 to concentrate on writing and speaking about non-controlling education and child-rearing. Data were collected based on the Academic Procrastination Scale (Solomon and Rothblum, 1984), a researcher-made comprehension test, and a timer, and the experimental group received brain-based teaching four times a week for eight sessions. Thirty people were randomly selected and grouped into two experimental (N=15) and control (N=15) groups. The population was students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity disorder in Gorgan in 2021. Method: This study was experimental with a pretest-posttest design and a control group.
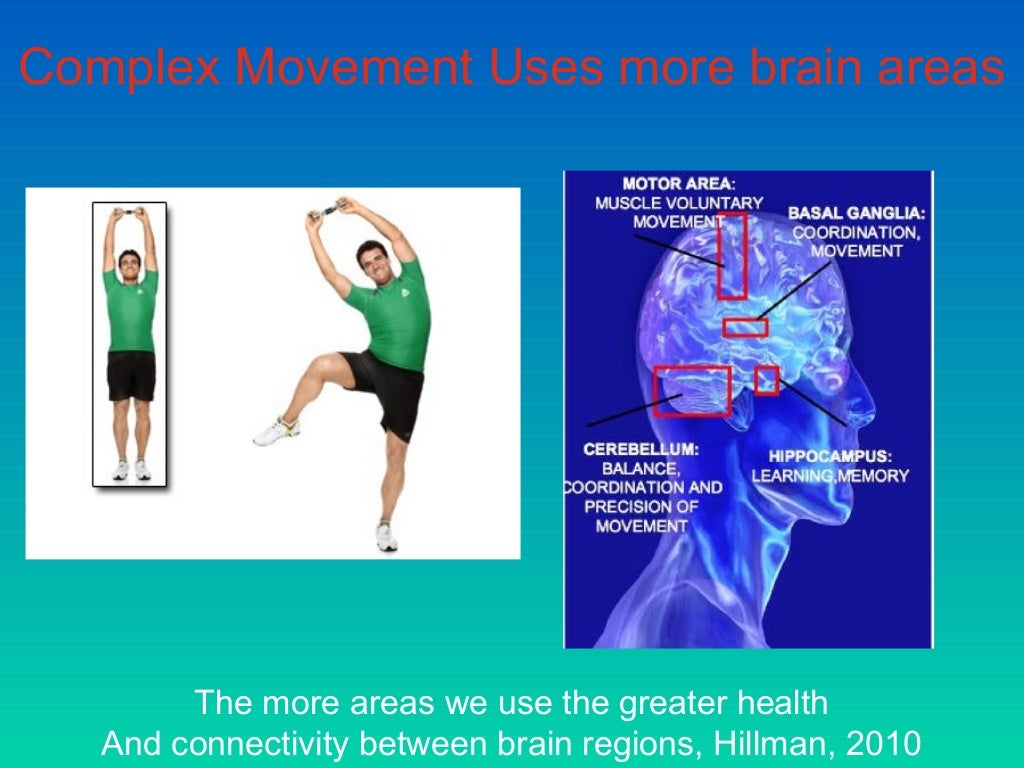
Introduction: Brain-based teaching is the purposeful application of brain function strategies for teaching that affect learning.Īim: The study evaluated the effectiveness of brain-based mathematics teaching on academic procrastination, comprehension, and learning rate of students with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity disorder. The conclusion is the experimental class 1 students have higher learning achievement than students in the experimental class 2. In science process skills, the experimental class-1 students had an average N-Gain score of 72,50, while the experimental-2 class was 60,88. Student learning outcomes experimental class-2 is 73,12. The results showed that the average value of the N-Gain score of student learning outcomes in the experimental class-1 was 80,72. The brain-based learning activities applied in this study are listening to music, drinking water, doing a brain gym, working on crossword puzzles, and group determination based on the dominance of students' brains. The data analysis technique used is the T-test. This research is a quasi-experimental study with a nonequivalent pretest-posttest control group design. The experimental class-1 is the class applied by PjBL with a brain-based STEAM approach, while the experimental class-2 is a class that uses PjBL with the STEAM approach without brain-based. This research was conducted in a special school for girls and used two experimental classes, namely experimental class-1 and experimental-2 class. The purpose of this study is to determine differences in student's learning achievement consisting of learning outcomes and science process skills.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
